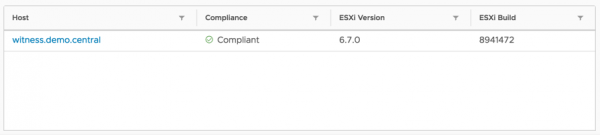
The vSAN Witness Appliance virtual machine provides a virtualized ESXi host that acts as a tie breaker for vSAN Stretched Cluster and 2 Node configurations. Some common questions come up around not only which version of the vSAN Witness Appliance should be used, but what version the vSAN Witness Appliance should be run on.
vSAN Witness Appliance
A few definitions first
With a few different items having “vSAN Witness” in their naming, this can get a bit confusing, so let’s clarify what each of these are, and what their role is.
- vSAN Witness Appliance – A free virtual appliance provided by VMware for use with Stretched Cluster or 2 Node vSAN configurations
- vSAN Witness Host – Either a physical ESXi system, or the vSAN Witness Appliance, being used to store tie-breaker metadata for a Stretched Cluster or 2 Node vSAN configuration
- vSAN Witness Component – A vSAN metadata component that is a used as tie breaker metadata for vSAN data components that reside on different fault domains or hosts.
It is important to understand their differences when deploying, configuring, or managing Stretched Cluster or 2 Node vSAN configurations.
Cluster Membership
vSAN Stretched Clusters, and 2 Node vSAN, require a vSAN Witness Host that “participates” in the vSAN Cluster. Participates is in quotes, because the vSAN Witness Host is not a traditional member of the cluster, and is only a vSAN Cluster member, not a vSphere Cluster member.
The general recommendation is to place the vSAN Witness Host in a different datacenter, such as Witness-Datacenter shown in the illustration above.
Notice that the vSAN Witness Host is not a member of the vSphere Cluster named Remote-Cluster.
Looking at the disk management UI of the vSAN configuration of Remote-Cluster, the disk group from the vSAN Witness Host is a contributing vSAN cluster member:
*Very important note: Do not attempt to make a cluster out of multiple vSAN Witness Hosts. They cannot be members of a vSphere Cluster.
If there is a need to “organize” vSAN Witness Hosts, use the Folder capability in the vSphere Client to organize them. Do not include them in a vSphere Cluster.
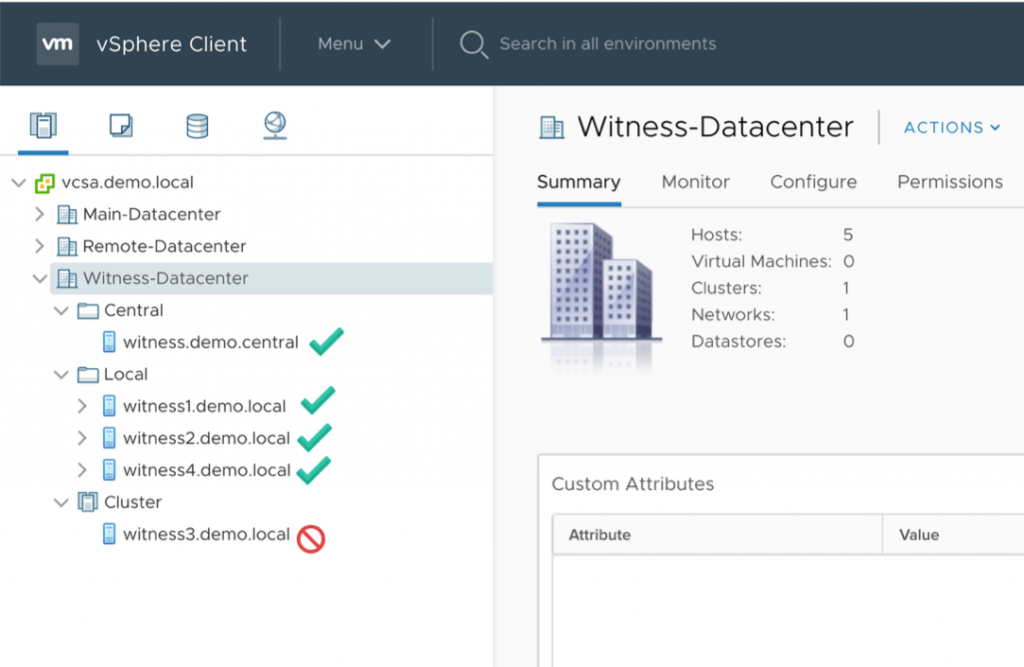
Notice that vSAN Witness Host “witness3.demo.local” is part of a vSphere Cluster. This is not supported.
Adding a vSAN Witness Host to a vSphere Cluster will require you to redeploy that vSAN Witness Host.
Versioning
Closer inspection of this sample 2 Node cluster shows that the data nodes are the same build, which is a recommended/supported configuration.
Although the vSAN Witness Host is not part of the vSphere Cluster, it is contributing disks to the vSAN Cluster. Because the vSAN Witness Host is contributing to vSAN, it is strenuously recommended to be the same build as the vSAN Data Nodes. It is generally required to be the same release of vSAN.
It is important to remember, that the vSAN Witness Host is an ESXi instance. Whether it is physical or virtual, it is patched the same as any other ESXi host.
Repeating that last statement for clarity: “Whether it is physical or virtual, the vSAN Witness Host is patched the same fashion as any other ESXi host.”
The illustrations above have only addressed the context of the vSAN Witness Host (which could be physical or virtual), and not the vSAN Witness Appliance.
Notice in the above illustration that the virtual machine WITNESS67 is running on host0.demo.local. This is the vSAN Witness Appliance that is provided by VMware for free.
This virtual machine has ESXi installed for use as a tie-breaker for the Remote-Cluster vSAN Cluster.
Its ESXi Guest OS is configured as witness.demo.central. The “virtual ESXi” is attached to the vCenter server. To vCenter, witness.demo.local appears (mostly) to be like any other ESXi installation.
Hosting the vSAN Witness Appliance
The guidance thus far has been that any vSphere 5.5 host, regardless of licensed edition, may be used for hosting a vSAN Witness Appliance. This is stated in the Stretched Cluster and 2 Node Guide on storageHub.vmware.com. This remains true today.
The vSAN Witness Appliance is generally supported on:
- Any on-premises or cloud hosted configuration provided appropriate connectivity is in place*.
- Any licensed edition of vSphere 5.5 or higher
- Any Free vSphere Hypervisor 5.5 or higher
*Refer to the Stretched Cluster and 2 Node Guide for more information around connectivity requirements.
With the release of vSphere 6.7 there are some new CPU requirements though, as vSphere 6.7 does not support the same list of CPUs as vSphere 5.5, 6.0, or 6.5. The vSphere 6.7 Release Notes detail CPUs that are no longer supported in vSphere 6.7.
In cases where the vSAN Witness Appliance is used for a vSAN 6.7 Stretched Cluster or 2 Node configuration, the vSphere Host’s CPU must also be supported by vSphere 6.7, regardless of the build of ESXi running on the vSphere Host.
Consider host3.demo.local which has a CPU that is not supported by vSphere 6.7. This host is running vSphere 6.5. It is still possible to deploy a vSAN Witness Appliance for vSAN 6.7 to a host that does not meet the requirements of vSphere 6.7.
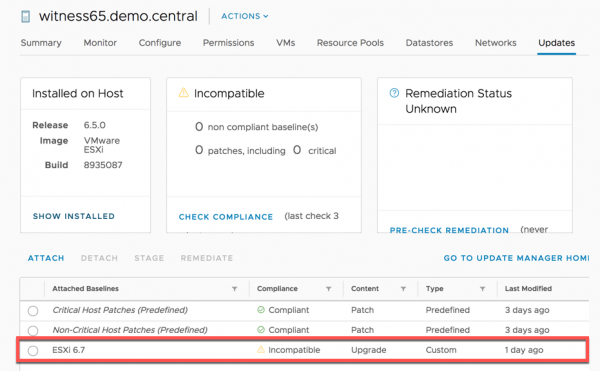
However, after deploying a new vSAN Witness Appliance for vSAN 6.7 to this host, and attempting to power it on, it can be seen that it is not allowed to boot.
Also, when attempting to patch/upgrade a previously deployed WITNESS65 (witness65.demo.central), which happens to be running on host3.demo.local it can be seen that it cannot be upgraded to vSphere 6.7.
This is because the host host3.demo.local does not have a CPU compatible with vSphere 6.7.
To successfully upgrade witness65.demo.central, the vSAN Witness Appliance (named WITNESS65) would have to be moved to a host that is compatible with vSphere 6.7.
Summing it all up
- vSAN Stretched Clusters and 2 Node configurations require a vSAN Witness Host.
- This can be a physical host
- This can be the vSAN Witness Appliance, a virtualized ESXi host, provided by VMware for free.
- A vSAN Witness Host should be the same build as the vSAN Stretched Cluster or 2 Node Configuration it is supporting
- This does not matter whether the vSAN Witness Host is physical or virtual.
- Update the vSAN Witness Host (physical or virtual) to the same build as the vSAN Data Nodes using VMware Update Manager or other approved method.
- If using the vSAN Witness Appliance (virtual), the location it runs on does not have to be the same build of ESXi.
- Example: A vSphere Cluster running vSphere 6.0 can run a vSAN Witness Appliance that has ESXi 6.5 installed “inside it”
- The vSAN Witness Host must have a CPU that is supported by the version of vSAN it is supporting
- If using a physical host, the CPU must be supported by the build of vSphere being used
- If using a vSAN Witness Appliance, regardless of the vSphere Host build it is being run on, ensure the vSphere Host CPU meets the requirements of the vSAN build it is supporting.
This was originally posted on the VMware Virtual Blocks site: https://blogs.vmware.com/virtualblocks/2018/07/05/witness-membership-versioning-hosting/